The introduction of 4G ushered in the era of the smartphone and hand-held mobile device. 4G was the first generation to use Long-Term Evolution (LTE) technology — which is displayed as LTE, LTE+ or LTE4G on devices. 4G/LTE has download speeds of 10Mbps to 1gigabits per second (Gbps) which equates to 1 billion bits of data per second, offering less buffering, improved voice quality, instant messaging services and social media, quality streaming, and faster download speeds.
4G/LTE is also the first IP-based mobile network which handles voice as just another service. The technology is being developed to accommodate the Quality of Service (QoS) and rate requirements required by applications such as wireless broadband access, MMS, video chat, mobile TV, HDTV content, Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB).
However, 4G networks soon began struggling with the heightened global demand for mobile bandwidth, higher speeds and faster networks due to emerging technologies — Augmented Reality (AR), autonomous vehicles and the exponential growth of the Internet of Things (IoT) — combined with the growing number of devices around the world.
In 2015, the International Telecommunications Union (ITU) realized 4G/LTE networks will ultimately reach capacity and defined requirements specification for 5G.
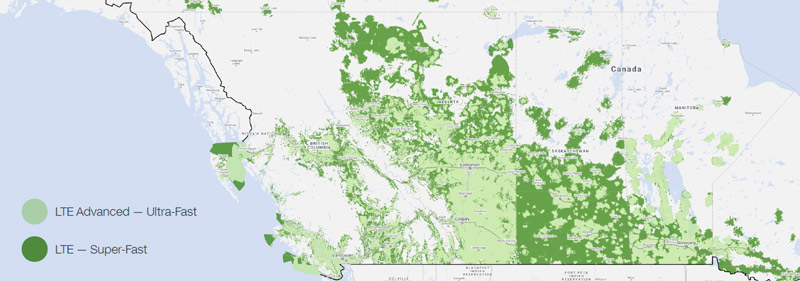
Telus 4G LTE3 Coverage Map. Coverage areas are approximate; actual coverage, network services and technology can vary and are subject to change. Source: TELUS.